Concussion Recovery Basics
Gradual Return to Activities
Updated Aug 2, 2019
Swipe right to go to the next slide
It is best to return to activities gradually after concussion by finding a balance between activity and rest.
In the past, complete rest for several days, weeks, or even longer, was often recommended. We now understand that complete rest for more than 48 hours after concussion is probably unhelpful and may prolong recovery.
On the other hand, overdoing it and pushing until you are forced to stop by worsened symptoms is also unhelpful.

You don’t have to be symptom free to begin gradually returning to activity. In fact, getting more active is a form of treatment rather than something you can only start doing after you have recovered. When considering how much activity is the right amount, it is helpful to think about three “Activity Zones”.
The Activity Zone diagram is based on the work of Dr. Mille Thastum and colleagues, with permission from the Hammel Neurorehabilitation and Research Centre, Denmark (Neurorehabilitation 2018, vol. 43, p. 155–67) .
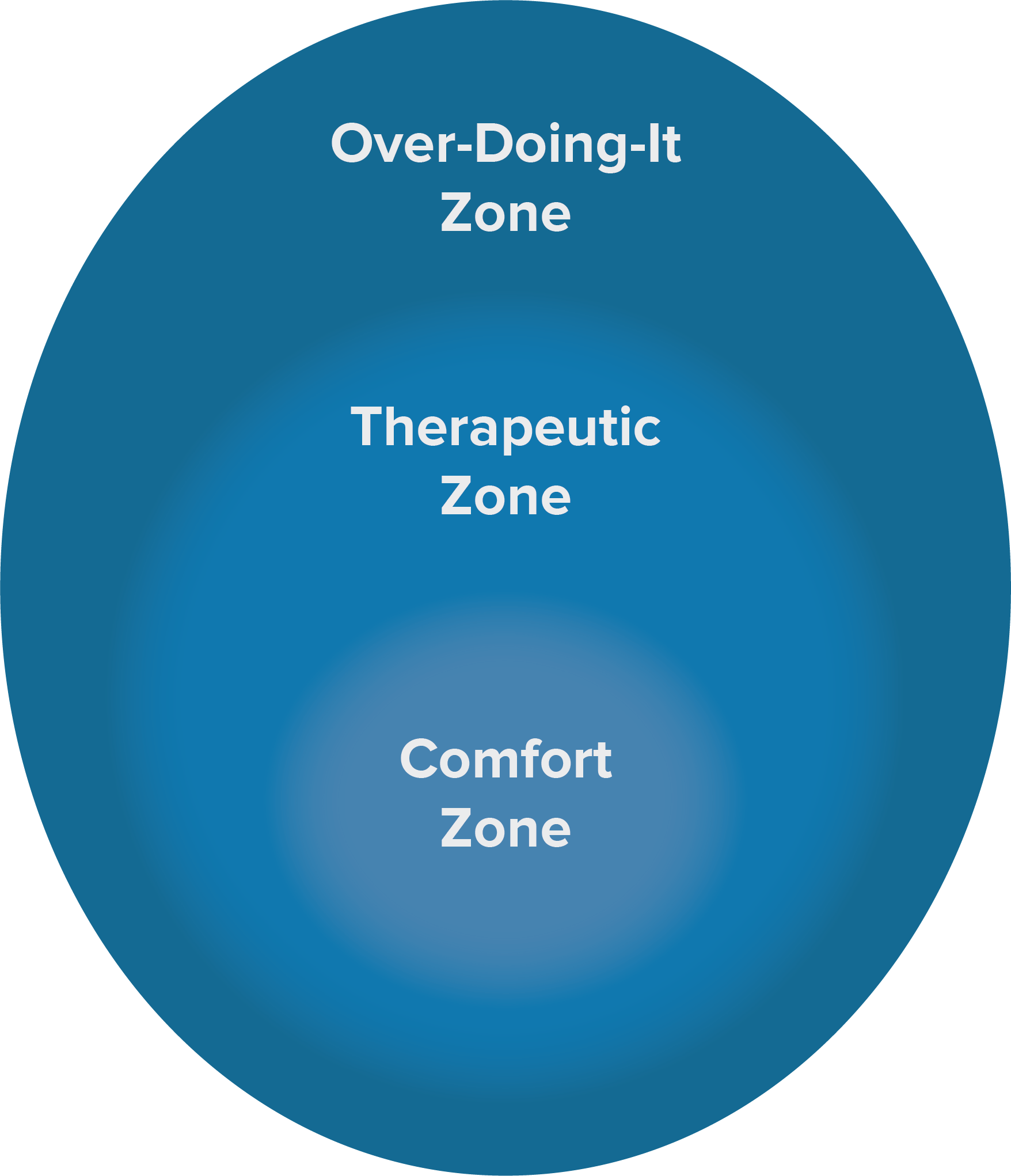
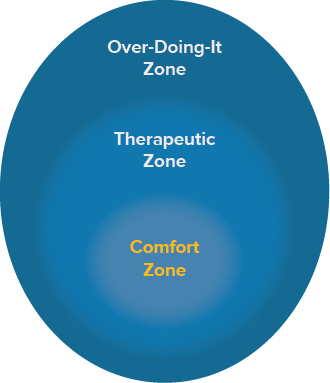
The inner circle is the “comfort zone.” In this zone, you are resting and not doing anything to increase symptoms. It’s tempting to stay in this zone for many reasons, including to avoid discomfort, fear, or a belief that “rest is best.”
However, spending too much time in the comfort zone can lead to physical deconditioning, social isolation, low mood, and reduced light and noise tolerance. These consequences can prolong recovery.
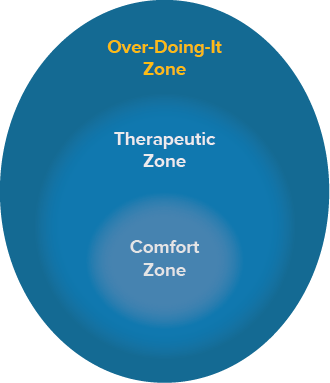
The outer circle is the “overdoing it zone,” where you push well past what you can tolerate, often leading to huge symptom spikes. You may enter this zone due to life demands, low awareness of when symptoms are increasing, or having no plan for gradually increasing activities.
Overdoing it is rarely harmful, but spending a lot of time in this zone can cause a cycle of pushing and then crashing. It can also cause intolerable symptom spikes.
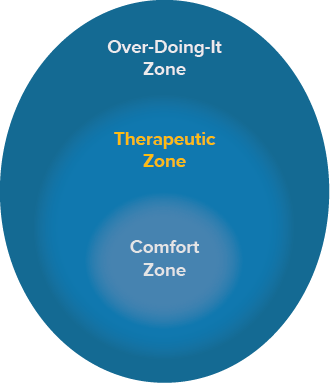
The middle area is the “therapeutic zone,” where you focus on activity that is a bit challenging but doable. You may experience mild symptom fluctuations, but not severe symptoms that impact your functioning the next day.
Returning to the comfort zone is fine sometimes, but you should try to be in the therapeutic zone most of the day. Taking a step out of your comfort zone is a step towards recovery. With time and practice, things that are a bit challenging now will become comfortable, and things that are too challenging now will become more realistic.
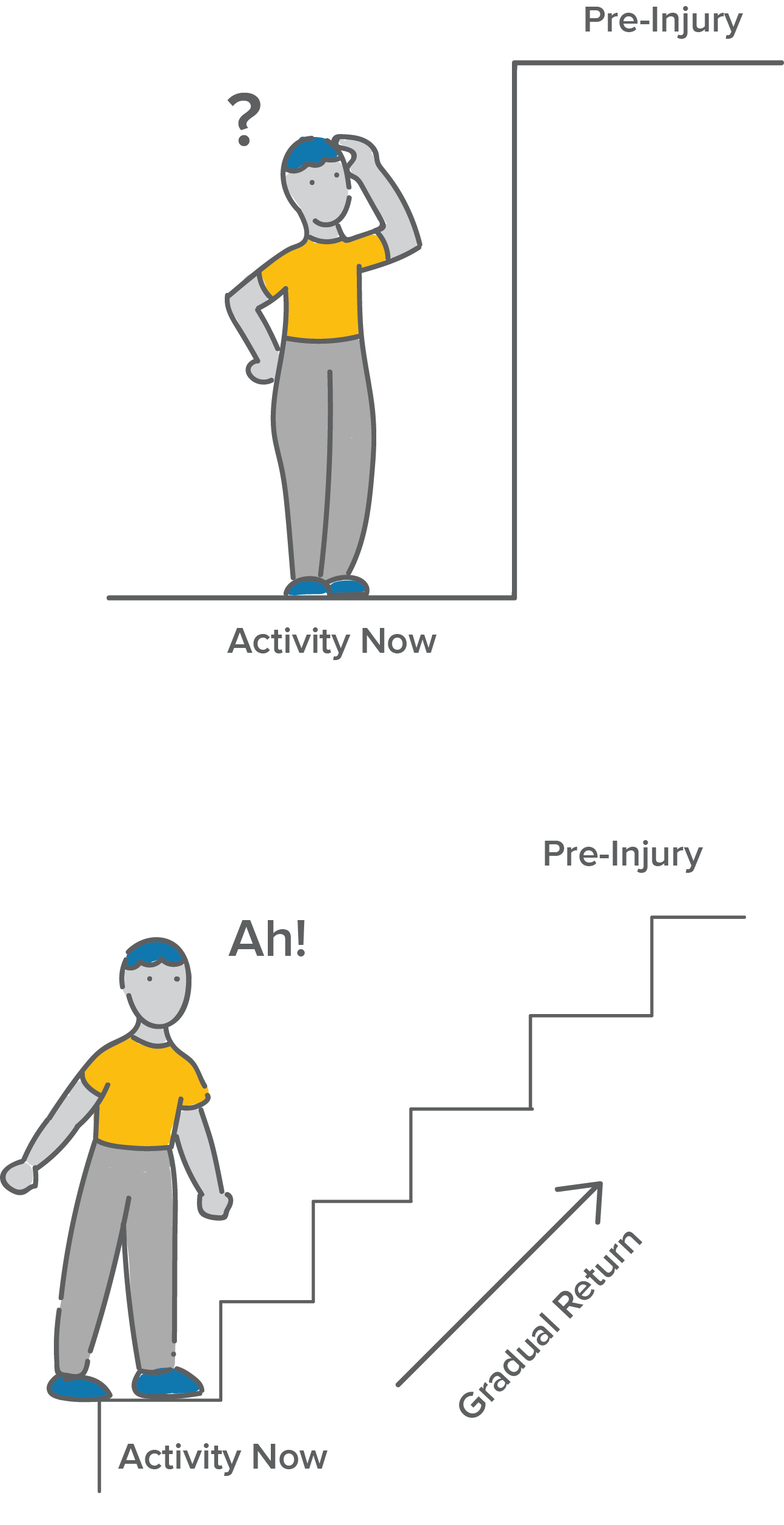
Returning to an activity is like a staircase you climb one step at a time.
What is comfortable for you right now? How often can you comfortably do the activity (frequency)? For how long (duration)? And at what intensity? This is your starting step.
Gradually move from your starting step by increasing frequency, duration, or intensity a little at a time. It is usually best to increase frequency first, then duration, and lastly intensity.
Concussion Awareness Training Tool (CATT) has created a very useful one-page graph [pdf] summarizing gradual return to activity. It might be useful to print this one-page document to remind you to take things step by step. Alternatively, you can download this printable copy of the Activity Zones diagram [png] to remind you to stay in the Therapeutic Zone.

Click the button above to toggle between light mode and dark mode. This toggle can also be found in the menu.
Hold
and tap
to zoom in.
Hold
and tap
to zoom out.
Hold
and tap
to zoom in.
Hold
and tap
to zoom out.
On most mobile devices, you can spread to zoom.
Increase your text size in your device settings.
Remember to take regular breaks while exploring MyGuide: Concussion.
Vancouver Coastal Health’s MyGuide Concussion Team would love to hear your feedback! It matters to us and helps to improve the experience for future users. Your responses will be kept anonymous and your privacy is a top priority. To complete a 15-20 minute online survey or request a telephone survey, please click the link below.